Example Of Transitive Property Of Congruence
Two column proof example using the transitive property. The three properties of congruence are the reflexive property of congruence the symmetric property of congruence and the transitive property of congruence.
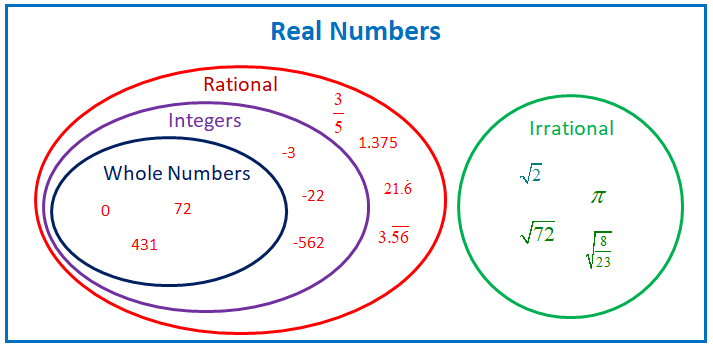
 High School Geometry Properties Of Congruence For Segments And Angles Geometry High School High School Segmentation
High School Geometry Properties Of Congruence For Segments And Angles Geometry High School High School Segmentation
If a b mod m and c d mod m then a c b d mod m and a c b d mod m.

Example of transitive property of congruence. Symmetric Property of Congruence b. If m 2 for instance these definitions say that x y y z and x z are even. For any angles A and B if A B then B A.
5 is equal to 5. The above three properties imply that mod m is an equivalence relation on the set Z. If a b and b c then a c.
A JK _____ b XY _____ Symmetric property of. We shall show that a cmodn. 3 rows Transitive Property of Congruence Examples.
AB CD then _____. JK LM then _____ Transitive property of. For any segment.
Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on equality properties. Yep that looks pretty true. Segments congruence is reflexive symmetric and transitive.
The Transitive Property for four things is. If two angles are both congruent to a third angle then the first two angles are also congruent. The relation over Z is transitive.
Using Transitive Property of Congruent Triangles. A a mod m 2. Reflexive Property of Equality c.
Transitive Property of Congruence EXAMPLE 1 Name Properties of Equality and Congruence In the diagram N is the midpoint of MP and P is the midpoint of NQ. Lets take a look at transitive property of. This is the transitive property at work.
If a b mod m and b c mod m then a c mod m. If giraffes have tall necks and Melman from the movie Madagascar is a giraffe then Melman has a long neck. The transitive property is like this in the following sense.
Transitive property of congruence The meaning of the transitive property of congruence is that if a figure call it figure A is congruent or equal to another figure call it figure B and figure B is also congruent to another figure call it C then figure A is also congruent or equal to figure C. The transitive property of congruence states that two objects that are congruent to a third object are also congruent to each other. Order of congruence does not matter.
Properties of congruence and equality Learn when to apply the reflexive property transitive and symmetric properties in geometric proofs. Thus triangle PQR is congruent to triangle ABC. The Transitive Property If you take a train from Belen to Albuquerque and then continue on that train to Santa Fe you have actually gone from Belen to Santa Fe.
Then a b kn k Z and b c hn h Z. If two segments or angles are congruent to congruent segments or angles then theyre congruent to each other. One example is algebra.
If you know one angle is congruent to another say and that other angle is congruent to a third angle say then you know the first angle is congruent to the third. In geometry we can apply the transitive property to similarity and congruence. The Transitive Property for three things is illustrated in the above figure.
By Transitive property of congruent triangles if ΔPQR ΔMQN and ΔMQN ΔABC then ΔPQR ΔABC. GH WO then _____ bIf. One way to remember the Reflexive Property of Equality is to think.
These properties can be applied to segment angles triangles or any other shape. Now lets look at an example to see how we can use this transitive property of equality to help us solve problems. To prove the transitivity property we need to assume that 1 and 2 are true and somehow conclude that 3 is true.
The following diagram gives the properties of equality. Reflexive symmetric transitive addition subtraction multiplication division and substitution. Solution MN 5 NP Definition of midpoint NP 5 PQ Definition of midpoint MN 5 PQ Transitive Property of Equality M N P P.
Show that MN 5 PQ. You may have two expressions that are equal that you are told are equal to a third algebraic expression which may allow you to potentially solve for missing variables. Examples If AB CD and CD EF then AB EF.
For any angles A B and C if A B and B C then A C. Reflexive property of. 1 and 2 say that m divides x y and y z.
The transitive property may be used in a number of different mathematical contexts. If a b mod m then b a mod m. We want to show that m divides x z.
Transitive Property for four segments or angles. Let a b c Z such that a bmodn and b cmodn.
Read more »Labels: congruence, example, property