Completeness Property Of Real Numbers Example
The following sets A x x Q x 0 x2 2 x x Q x 0 B Q A are the most popular example of such a partition. Real numbers are simply the combination of rational and irrational numbers in the number system.
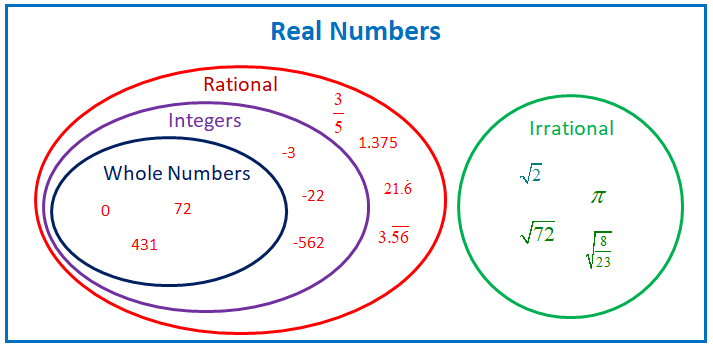
 Are You Teaching Your Middle School Math Students About The Real Number System This Product Incl Real Number System Number System Worksheets Rational Numbers
Are You Teaching Your Middle School Math Students About The Real Number System This Product Incl Real Number System Number System Worksheets Rational Numbers
Any nonempty subset of R that is bounded.
Completeness property of real numbers example. At the same time the imaginary numbers are the un-real numbers which cannot be expressed in the number line and is commonly used to represent a complex number. Each nonempty set of real numbers that has an upper bound has a least upper bound. A fundamental property of the set R of real numbers.
Example 124 The minimum of 01 is 0. But if we take an example. Then u infS1 andw supS1.
This property is sometimes called Dedekind completeness. On the other hand the system of real numbers possesses completeness in the sense that any partition of the real numbers into two. It doesnt work in.
8S R and S6 If Sis bounded above then supSexists and supS2R. That is the set Shas a least upper bound which is a real number. Show that there exist n 1 n 2 N n_1n_2 in N n 1 n 2 N such that α α 1 n 1 β alpha.
The least-upper-bound property is an example of the aforementioned completeness properties which is typical for the set of real numbers. 3 and 11 are real numbers. In general all the arithmetic operations can be performed on these numbers and they can be represented in the number line also.
This means that if a number fits in the natural numbers it can also be classified as a whole number integer rational and real number. In other words the Completeness Axiom guarantees that for any nonempty set of real numbers Sthat is bounded above a sup exists in contrast to the max which may or may not exist see the examples above. R has no gaps.
And 3 dac dab dbc for any real numbers a b and c. Completeness is the key property of the real numbers that the rational numbers lack. Suppose LH R L 6 6 H and h 82Lh 2H Since L 6 and L is bounded above by any element of H supL exists and it is a real number so let supL.
It does not have a maximum. The completeness axiom for the real numbers states that any subset of the reals that is bounded above has a supremum. Thus we would have.
The Completeness Axiom distinguishes the set of real numbers R from other sets such as the set Q of rational numbers. Completeness of the real numbers - Least upper bound property Consider a set of rational numbers x such that x 2 2. This distance function has the following properties.
Chapter 1 The Real Numbers 11 The Completeness Property of R Example 111 Bartle 235 a Page 39. Let A fr2Qj0 r p 2g Q. Examples are 1 2 3 4 1567 12456.
The distance between two real numbers a and b is defined to be the absolute value of their difference dab a b. A nonempty set S1 with a finite number of elements will have a least element sayu and a largest element sayw. By the denition of supremum is an.
Example 123 The smallest element or minimum of 01 is 0Its largest element or maximum is 1. The properties of real numbers can be Commutative Associative and Distributive and usually consist of algebraic expression like a b and c along with real numbers. 2 dab dba.
Examples include ac ca or. Assume the Supremum Property and show that the completeness axiom holds. Each nonempty set of real numbers.
More generally if aand bare two real numbers such that a bthen minab aand maxab b. Before examining this property we explore the rational and irrational numbers discovering that both sets populate the real line more densely than you might imagine and that they are inextricably entwined. Axiom 7 Least upper bound axiom.
Any nonempty subset of R that is bounded above has a least upper bound. There are various di erent logically equivalent statements that can be used as an axiom of the completeness of the real numbers. To be a maximum a number would have to be in 01.
1 dab 0 and dab 0 only if a b. Real numbers are closed under addition subtraction and multiplication. Well use one called the least upper bound axiom.
3 11 14 and 3 11 33 Notice that both 14 and 33 are. Suppose that α β alphabeta α β are two real numbers satisfying α β alpha. 51 Rational Numbers Definition A real number is rational if it can be written in the form p q where p and q are integers.
If an ordered set has the property that every nonempty subset of. An analogous property holds for inf S. But then 1 2.
That means if a and b are real numbers then a b is a unique real number and a b is a unique real number.
Read more »Labels: completeness, example, real
