What Is An Inherent Risk Factor
You consider the strength of the. Identify whether each factor was an inherent risk factor.
Inherent risk - Measure of auditors assessment of likelihood of material misstatements before considering effectiveness of internal control - Inversely related to PDR directly related to evidence - Assessment of inherent risk affects amount of evidence assignment of staff review of.

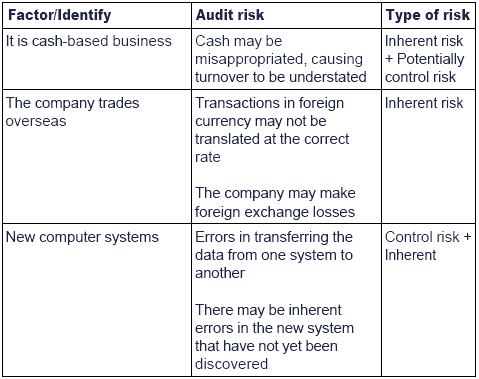
What is an inherent risk factor. While assessing this level of risk you ignore whether the client has internal controls in place such as a secondary review of financial statements in order to help mitigate the inherent risk. Inherent risk is current risk level given the existing set of controls rather than the hypothetical notion of an absence of any controls. Inherent risk factors include uncertainty change and fraud risk and more.
Inherent risk is the risk posed by an error or omission in a financial statement due to a factor other than a failure of internal control. Inherent risk is common in cases involving complex financial instruments or where an accountant has to apply an unusually high degree of approximation or judgement. The spectrum of inherent risk is affected by the inherent risk factors.
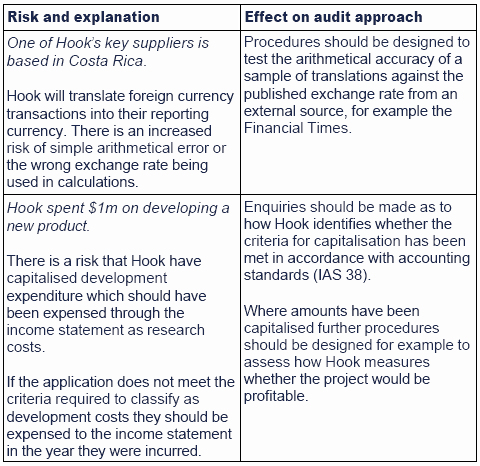
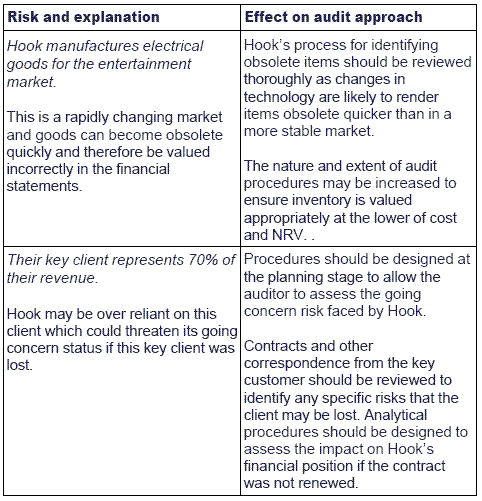
Inherent risks cause by external factors rather than internal factors. Nature of the Clients Business An entity in the fast-changing high-technology industry faces a risk of inventory obsolescence. Rapid innovations can cause the entitys products to.
The Five Inherent Risk Factors Overview This discussion introduces the five inherent risk factors that impact major public sector procurement projects and explains how these factors contribute to overly optimistic planning assumptions and impose unrealistic expectations on major project teams. Factors Affecting Inherent Risk There are many factors affecting a client entitys inherent risk. It gives you an indication of the.
Additionally there is a. Indicate whether the factor affected their assessment of inherent risk at the financial statement or. One type of risk to be aware of is inherent risk.
Inherent risk as applied to the practice of accounting is the risk of wrong or misleading information appearing in financial statements that have occurred for reasons other than the failure of. In a financial audit inherent risk is most likely to. The auditors were required to.
Inherent Risk is the risk of a material misstatement in the financial statements arising due to error or omission as a result of factors other than the failure of controls factors that may cause a misstatement due to absence or lapse of controls are considered separately in the assessment of control risk. If nothing changes related to that risk the business faces failure. The draft also introduces the concept of a spectrum of inherent risk which is the degree that inherent risk varies.
When applied to an organizations financial statements inherent risk can usually be broken down into fraud and failure risks. Inherent risk is the risk associated with a given engagement regardless of the controls the vendor has implemented. Residual risk would then be whatever risk level remain after additional controls are applied.
Inherent risk may be defined as the risk of an error omission or misleading information in a financial statement arising from such factors other than a failure of controls. In business the term inherent risk refers to the danger of failure that a business faces due to factors that are essential to operations. As we mentioned above inherent risks are the risks that the financial statements could contain material misstatements on an account or group of accounts that are pervasive to financial statements.
 Don T Succumb To The Vicious Temptation Of Overtrading It Kills Your Account Forex Makemoney Trading Trading Quotes Day Trading Forex Trading Strategies
Don T Succumb To The Vicious Temptation Of Overtrading It Kills Your Account Forex Makemoney Trading Trading Quotes Day Trading Forex Trading Strategies
 Basics Of 4 20ma Current Loop Control Engineering Loop Basic
Basics Of 4 20ma Current Loop Control Engineering Loop Basic
 Management Vs Leadership In 2021 Leadership Business Leadership Management
Management Vs Leadership In 2021 Leadership Business Leadership Management
 Presentation 3 Fine Tuning Elements Of System Based Auditing Worksh Audit Microbiology System
Presentation 3 Fine Tuning Elements Of System Based Auditing Worksh Audit Microbiology System
 Why Salestraining Fails And Your Options By Peak Performance Training And Development By Peak Performa Training And Development Sales Training Peak Performance
Why Salestraining Fails And Your Options By Peak Performance Training And Development By Peak Performa Training And Development Sales Training Peak Performance
 Project Selection And Portfolio Management Which Project Should Be Supported How Can We Manage Simulta Portfolio Management Risk Analysis Senior Management
Project Selection And Portfolio Management Which Project Should Be Supported How Can We Manage Simulta Portfolio Management Risk Analysis Senior Management
 Bearce Insurance Agency Here To Help Life Insurance Policy Insurance Insurance Agency
Bearce Insurance Agency Here To Help Life Insurance Policy Insurance Insurance Agency
 Continuous Improvement High Roi Initiatives Change Management Operational Excellence Strategy Map
Continuous Improvement High Roi Initiatives Change Management Operational Excellence Strategy Map
 Consulting Workshop Series Scenario Planning Business Case Template Strategic Goals Strategic Planning Process
Consulting Workshop Series Scenario Planning Business Case Template Strategic Goals Strategic Planning Process
 C I Of Bone Marrow Biosy Note Sevre Thrombocytopenia Alone Is Not A Contraindicati Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Radiation Therapy Intravascular
C I Of Bone Marrow Biosy Note Sevre Thrombocytopenia Alone Is Not A Contraindicati Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Radiation Therapy Intravascular
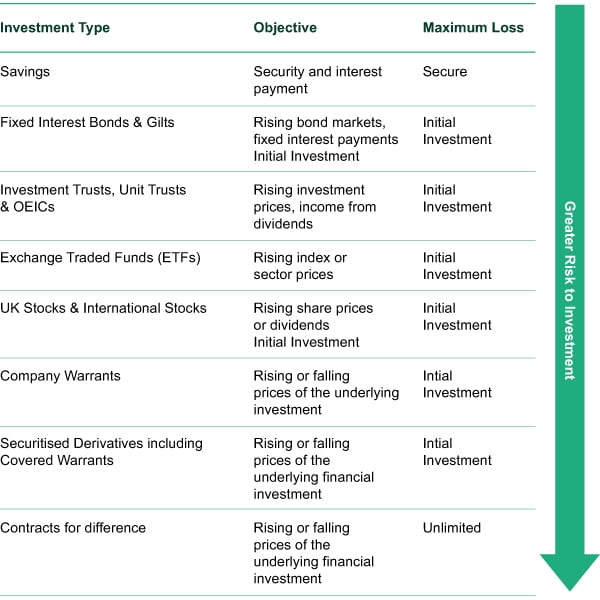 5 Key Factors That Can Affect Your Investment Risk Tolerance
5 Key Factors That Can Affect Your Investment Risk Tolerance
 Human Factors In The Design Control Process 5 Gu E 5 U A Acto S T E Es G Co T O Ocess Contextual Inquiry Literatur Task Analysis Training And Development Human
Human Factors In The Design Control Process 5 Gu E 5 U A Acto S T E Es G Co T O Ocess Contextual Inquiry Literatur Task Analysis Training And Development Human
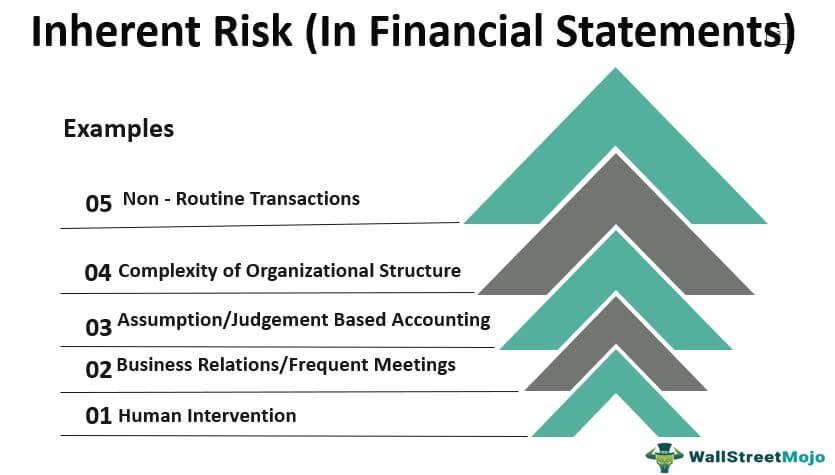 Inherent Risk Definition Types Top 5 Examples
Inherent Risk Definition Types Top 5 Examples
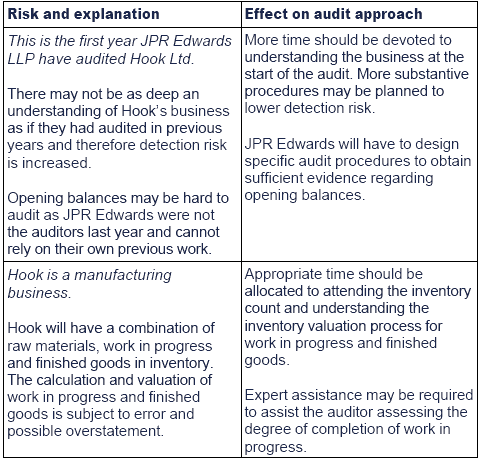
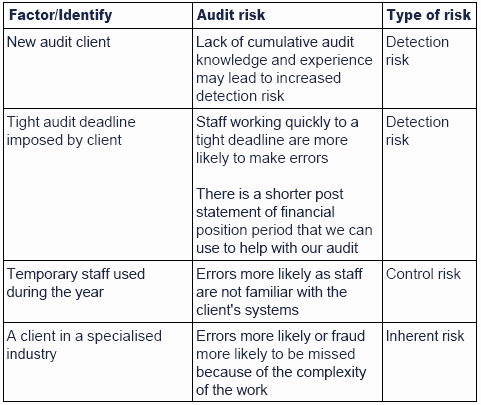



0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home